- Key performances indicator - measure that are tied to business drivers.
- Metrics are detailed mesures that feed KPIs
- Performances metrics fall into the business intilligence that is neither technology, nor business centered , but requires input from both IT and business professionals.
EFFICIENCY AND EFFECTIVENESS
- Efficiency IT metric - measures the performances of the IT system itself including throughput, speed, and availability.
- Effectiveness IT metric - mesures the impact IT has on business processes and activities including customer satisfaction, conversion rates, and sell-through increase.
BENCHMARKING- BASE LINE METRICS
- Benchmarking - a process of continously measuring systems results, comparing those results to optimal systems performances, and identfying steps and procedures to improve system performance.
BENCHMARKING - BASELINING METRICS
- E-government bencmarking
EFFICIENCY IT METRICS
- Efficiency IT metrics focus on technology and include
- Throughput - the amount of information that can travel through a system at any point
- Transaction speed - the amount of time a system takes to perform a transaction.
- System availability - the numbers of hours a system is available for users.
- Information accuracy - the extent to which a system generates the correct results when executing the same transaction numerous time
- Web traffic - includes a host of bencmarks such as the number of page views, the number of unique visitors, and the average time spent viewing a web page.
- Response time - the times it takes to response to user interactions such as a mouse click.
EFFECTIVENESS IT METRICS
- Effectiveness IT metrics focus on an organization's goals ,strategies, and objectives and include :
- Usability - the ease with which people perform transactions and/or find information. A popular usability metric on the internet is degrees of freedom,which measures the number of clicks required to find desired information.
- Customer satisfaction - measured by such benchmarks as satisfaction surveys , percentage of existing customers retained, and increases in revenue dollars per customers.
- Conversion rates - the number of customers an organization "touches" for the first time and persuades to purchase its products or services .This is a popular metric for evaluating the effectiveness of banner, pop-up, and pop-under ads on the internet.
- Financial - such as return to investment, cost-benefit analysis.
THE INTERRELATIONSHIP OF EFFICIENCY AND EFFECTIVENESS IT METRICS
METRICS FOR STRATEGICS INITIATIVES
- Metrics for measuring and managing strategis initiative include :
- Web site metric
- website metric include:
*Abandoned registrations - number of visitors who start the process of completing a
registration page and then abandon the activity.
*Abandoned shopping carts - Number of visitors who create a shopping cart and start
shopping and then abandone the activity before paying
for the merchandise.
*Click-through - count of the number of people who visit a site, click on an ad, and are
taken to the site of the advertiser.
*Conversion rate - percentage of potiential customers who visit a site and acctually buy
something.
*Cost-per-thousand (CPM) - sales dollars generated per dollar of advertising.This is
commonly used to make the case for spending money to
appear on a search engine.
*Page exposures - average number of page exposures to individual visitors.
*Total hits - number of visit to a website, many of which may be by the same visitor
*Unique visitors - number of unique visitors to a site in a given time.This is commonly
used by Nielsen/Net ratings to rank the most populat web sites.
- Supply chain management (SCM) metrics
*Back order - an unfilled customers order .A back order is demand against an item
- Customer realationship management (CRM) metrics
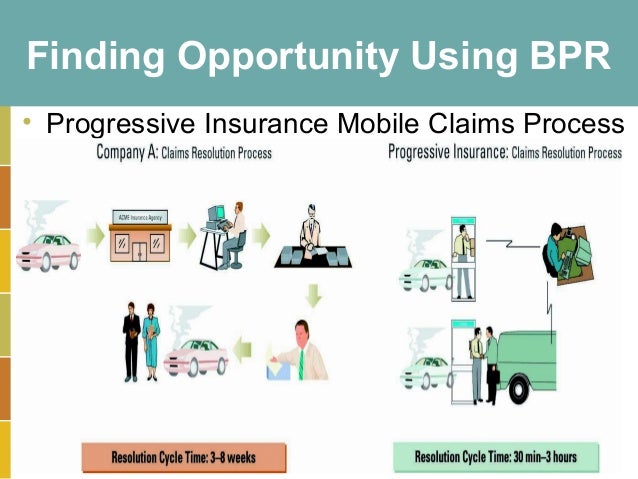
- Business process reengineering (BPR) mterics
- Enteprise resources planning (ERP) metrics.